Definition and Purpose of SEO and GEO
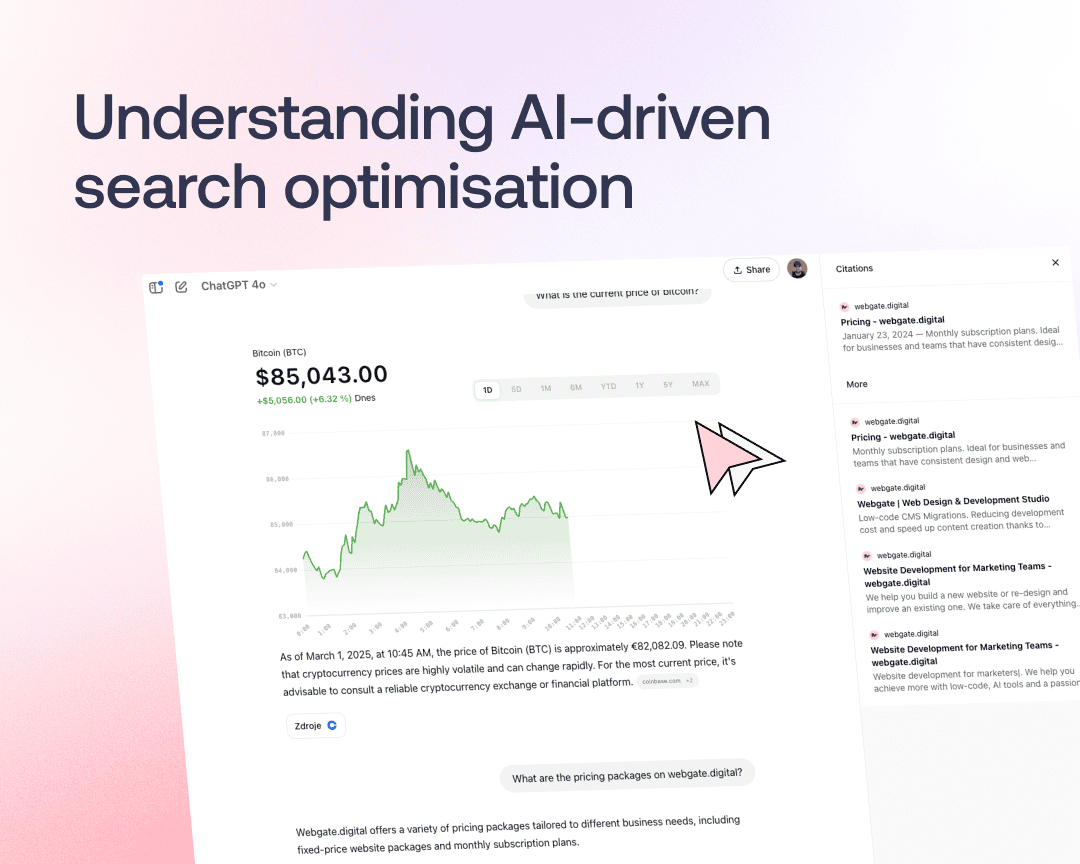
As artificial intelligence transforms how people search for information, businesses must adapt their strategies to stay visible.
Some interesting statistics:
“Gartner predicts a significant drop in traditional search volume by 25% by 2026, with organic search traffic expected to decrease by over 50% as consumers embrace AI-powered search.”
“Additionally, 79% of consumers are expected to use AI-enhanced search within the next year, and 70% already trust generative AI search results.”
Traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has long been the foundation of digital visibility, helping websites rank higher on Google and other search engines. However, with the rise of AI-powered search assistants like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), Bing Chat, and ChatGPT, a new approach called Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is emerging.
While SEO focuses on ranking well in search engine results pages (SERPs), GEO is about ensuring your content is featured in AI-generated answers.
As more users turn to AI-driven searches for direct responses rather than clicking links, brands need to optimize their content to be cited, summarized, and referenced by AI models.
This shift demands a new approach to content creation—one that prioritizes clarity, authority, and structured information that AI can easily interpret and present to users.
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
SEO is the long-standing practice of improving a website’s content and structure to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs).
The goal is to increase organic visibility and traffic from search engines like Google or Bing by aligning with their ranking algorithms. SEO tactics include using targeted keywords, producing high-quality relevant content, and building authoritative backlinks, all to signal to the search engine that a page is the most relevant result for a given query. In essence, the purpose of SEO is to make your site more visible and attractive to traditional search engines so that users searching for information will find and click on your website.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
GEO stands for Generative Engine Optimization – a newer concept emerging in response to AI-driven search tools. Its purpose is to ensure your content is discoverable and prominently featured in answers generated by AI generative engines (like ChatGPT, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), Bing Chat, Claude, Google Gemini, Perplexity, etc.).
Instead of just producing a link in a list of results, GEO aims to have your content included or cited in the AI’s composed answer when users pose questions related to your domain.
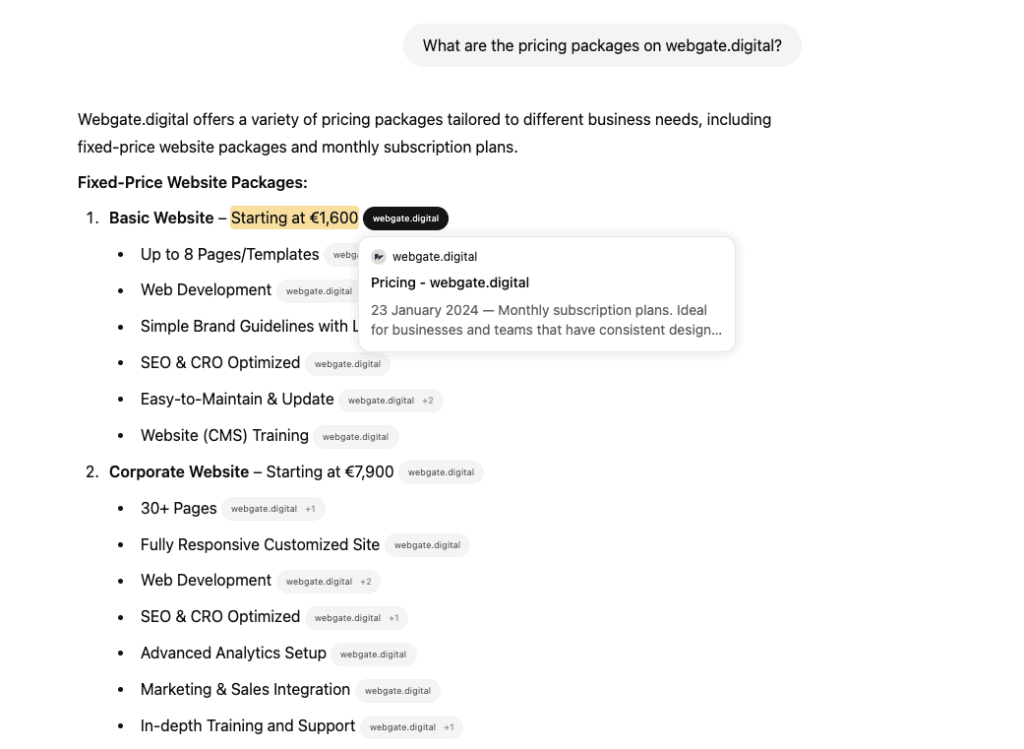
For example, GEO involves optimizing your site’s content so that if someone asks an AI, “What’s the best CRM for small e-commerce businesses?”, the AI will mention or quote your brand’s content in its answer.
In short, GEO’s purpose is to “maximize reach and visibility inside generative AI engines” – making sure the AI understands your content and can use it to answer relevant user queries. This way, even as users get direct answers from AI, your brand’s expertise and offerings remain part of the conversation.
What Are The Key Differences and Similarities between SEO and GEO?
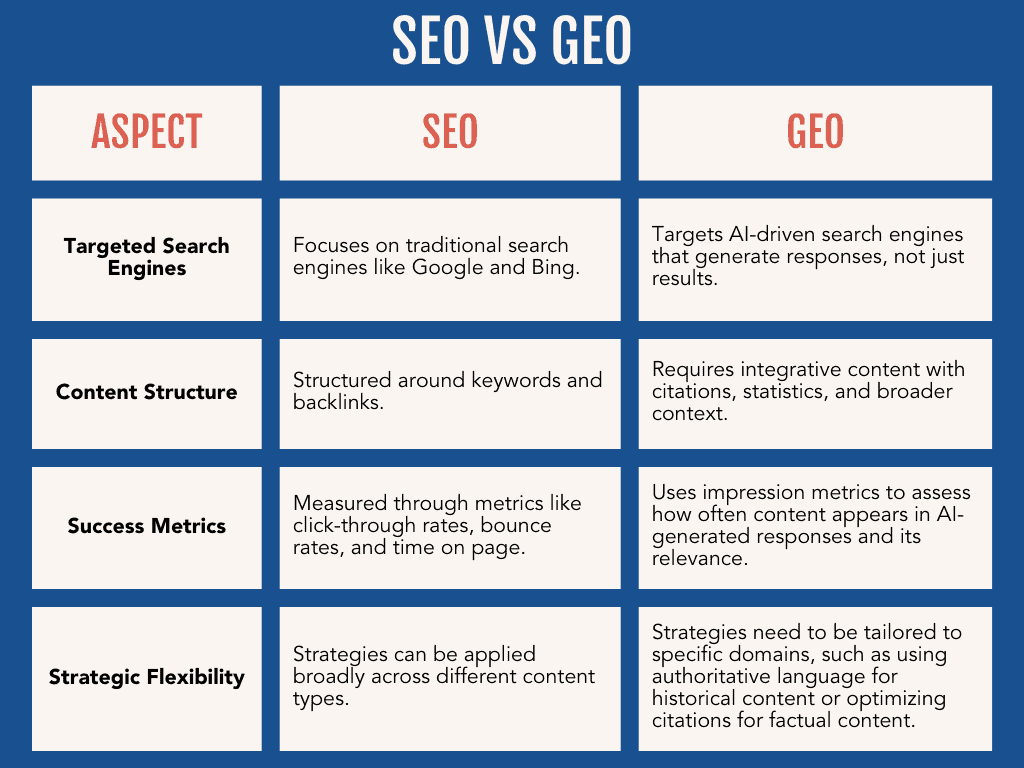
SEO and GEO both seek to connect users with relevant information, but they do so in different arenas. Below are key differences (and a few similarities) between traditional SEO and the emerging GEO approach:
Where Results Appear: SEO focuses on improving rankings in the search engine results page (SERP) – essentially the list of links a search engine returns. In contrast, GEO targets visibility within the generated answers that AI search tools provide. In other words, SEO tries to get you to the top of Google’s links, whereas GEO tries to get you mentioned or cited by the likes of an AI assistant in its response.
Primary Goal: The primary goal of SEO is to drive organic traffic to your website by ranking high for relevant queries.
GEO’s primary goal is to achieve brand presence in AI-driven answers – ensuring the AI cites your content or brand when answering questions. Both ultimately aim for visibility, but one is via clicks on links, and the other is via inclusion in an AI’s narrative.
Optimization Focus: Traditional SEO optimizes for keywords, metadata, and backlinks – essentially signals that search algorithms use to rank results.
GEO, on the other hand, optimizes for context and clarity so that AI models correctly interpret and trust the content. For example, while an SEO strategy might emphasize inserting a keyword phrase multiple times and earning links to a page, a GEO strategy emphasizes providing clear answers, authoritative context, and even structured data that an AI can easily parse and quote.
Content Format and Style: SEO has often rewarded longer-form content (think of those 2,000-word blog posts targeting every related keyword) and technically optimized pages.
GEO favors content that is concise, answers questions directly, and is formatted in a way an AI can digest. It’s less about length and more about being to the point and factually rich: for instance, a GEO approach might involve a Q&A style article or a clearly structured FAQ section that an AI can pull a direct answer from. Including facts, definitions, or step-by-step solutions that an AI could quote verbatim is especially useful. (Notably, one study found that content containing quotations, citations, or statistics saw significantly higher inclusion in AI responses – in some cases boosting visibility by over 40%.)
Success Metrics: In SEO, success is measured by metrics like organic traffic, click-through rates (CTR), and conversion from search visitors.
In GEO, success is measured by presence in AI outputs – e.g. how often your brand/content gets mentioned by generative engines, and whether users subsequently engage with your brand (even if they don’t click a link immediately). This means tracking things like citations in AI, brand mentions, or traffic coming from AI chat referrals (for instance, a user clicking a source link in a Bing Chat answer).
Authority Signals: For SEO, having other websites link to you (backlinks) has been a core signal of authority and trust. In GEO, the “authority” might come from overall web consensus and context – for example, being mentioned across forums, reviews, or having your information corroborated by multiple sources helps an AI judge its reliability. In practice, this means user-generated content (forum posts, Q&A sites, reviews) that mention your brand or content can indirectly boost your visibility in AI answers, much like backlinks do for Google.
Similarities:
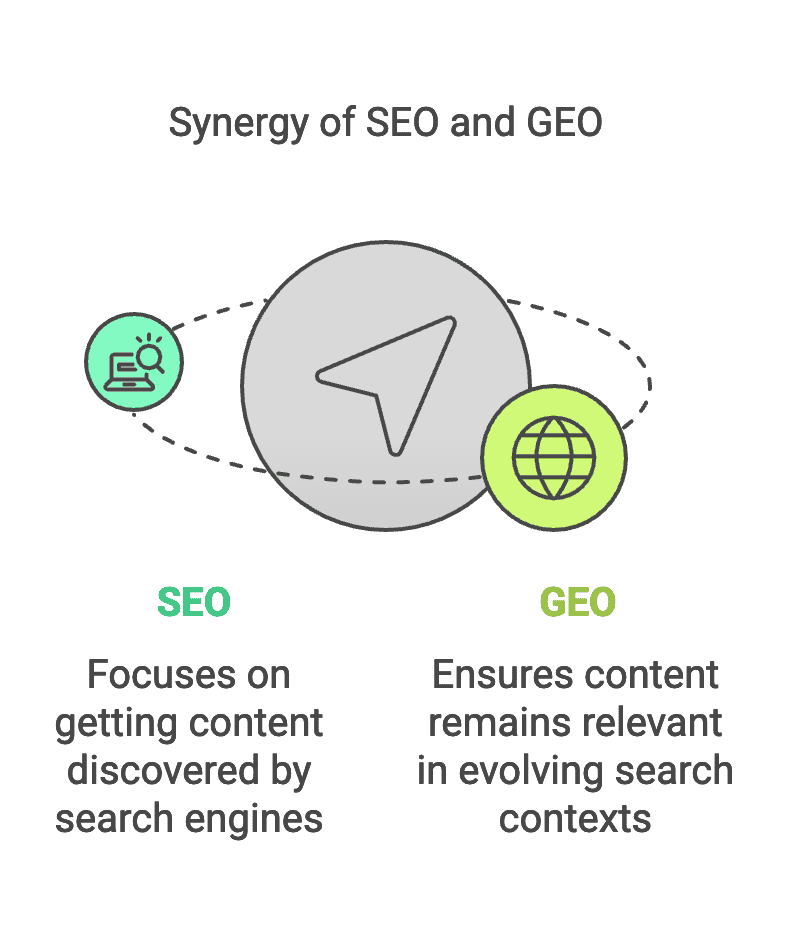
Both SEO and GEO ultimately depend on providing useful, relevant content to the end-user. In fact, they complement each other more than they conflict. Strong content quality and a good understanding of user intent are crucial in both approaches. Many SEO fundamentals – clear site structure, logical headings, fast loading speeds, etc. – also support GEO, because they make it easier for any engine (human-coded or AI) to understand and trust your site. It’s not an either-or situation: digital marketers are finding that traditional SEO and GEO efforts must cross over and work in tandem.
Both aim to “serve the right content to the right users at the right time,” and a solid content strategy will naturally improve performance in both organic SERPs and AI-driven results. In short, SEO gets your content on the map, and GEO helps keep it in the conversation as search evolves.
Example: To illustrate the difference, imagine a local Italian restaurant. Using SEO, the restaurant might try to get their website to rank #1 for “best Italian restaurant in [City]” by adding that keyword to their homepage and earning foodie blog backlinks. Using GEO, the restaurant would focus on ensuring an AI like ChatGPT or Google’s SGE recognizes what makes them unique.
They might publish a detailed menu page and blog posts answering questions like “Which restaurant in town has authentic homemade pasta?” or “What are the must-try dishes at an Italian restaurant?”. If done well, when a user asks an AI “Where can I get authentic homemade pasta in town?”, the AI’s answer will confidently mention that restaurant (maybe citing a review or the restaurant’s own content), even if the restaurant’s website isn’t the top traditional Google result. This example shows how GEO can put a business in front of customers via AI recommendations, not just search engine links.
Techniques and Best Practices for Implementing GEO
Optimizing for generative AI requires a shift in content strategy and some new tactics. Here are key techniques and best practices for implementing GEO on your website:
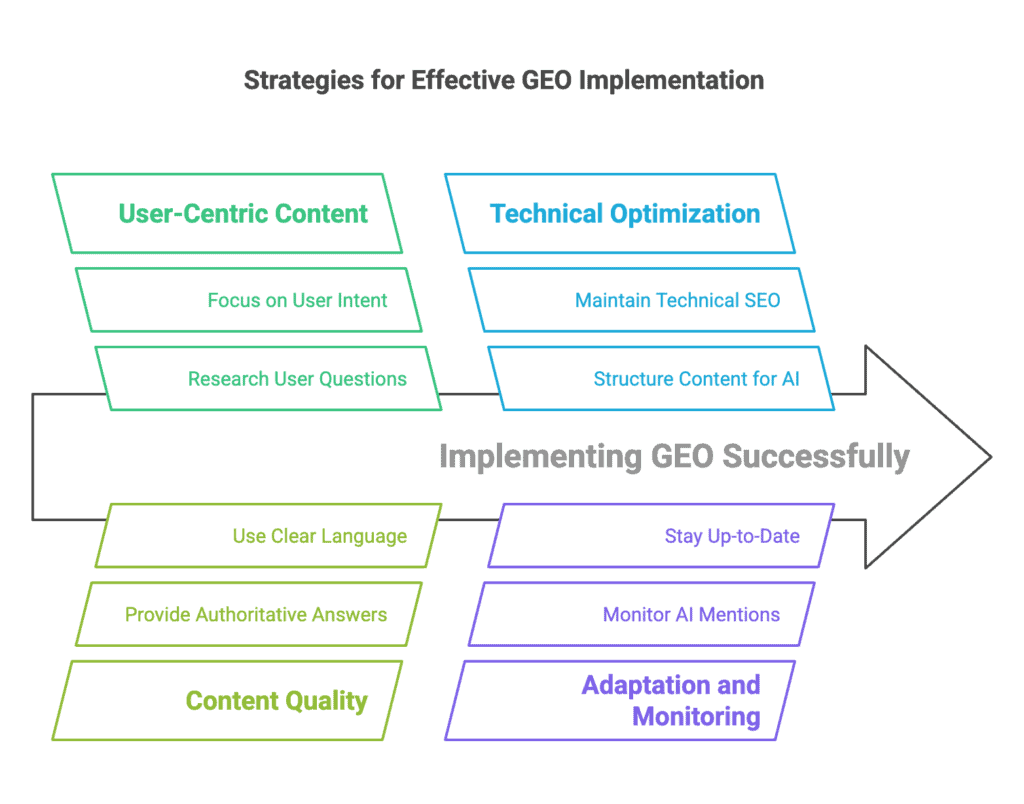
Research the Questions Users Ask: Start by identifying the real questions and long-tail queries your target audience has. This goes beyond traditional keyword research – you want to know what problems or queries people might pose to an AI. Leverage tools and data sources like customer support logs, forums (Reddit, Quora), or tools like AnswerThePublic to find common questions in your niche. For example, if you sell coffee machines and people often ask support “How long does it take to heat up?” or “What’s the cost per cup?”, those are golden topics to address on your site. By basing your content on actual user questions, you increase the chance an AI will find your content relevant when a similar question is asked.
- Provide High-Quality, Authoritative Answers: Create or refine content that directly answers those questions in a clear, accurate, and detailed manner. Each piece of content (be it a blog post, FAQ page, or guide) should be crafted as if you are answering the user personally. Include reputable sources, facts, or quotes to support your points – this not only builds trust with readers but also makes AIs more likely to incorporate content that is backed by data or notable quotes.
- Write in an authoritative tone and demonstrate expertise (e.g. cite your experience or industry knowledge) so the AI recognizes your content as trustworthy. The content should thoroughly cover the topic so that the AI has plenty of context to draw from.
Use Clear, Easy-to-Parse Language: Generative AI prefers content it can easily interpret and even quote.
- Avoid jargon or overly complex language – write in clear, concise sentences as if explaining to a smart friend outside your industry. For instance, instead of saying “We leverage cutting-edge methodologies to maximize operational efficiency,” say “We help businesses save time by automating their daily tasks.”. The simpler, more direct phrasing is not only better for users, but also for AI parsing.
- Aim for a conversational yet informative tone, which fits well when an AI delivers it in answer form.
Structure Your Content for AI Comprehension: Just as good formatting helps with SEO, it’s critical for GEO. Organize content with descriptive headings and subheadings that clearly signal what each section is about. Use lists or bullet points to break down steps or key points (AI often likes to present answers as lists). Start sections with a brief summary sentence that an AI might directly quote. Also use schema markup (structured data) where appropriate to explicitly label elements like FAQs, how-tos, product details, etc.. This additional structure provides context to AI models about your content’s meaning. Essentially, make your page machine-friendly – easy for a crawler or language model to extract Q&A pairs, definitions, or other logical chunks.
Focus on User Intent and Context: Always consider why a user is asking a question. Generative AI tries to satisfy the intent behind a query. Ensure your content actually fulfills the user’s need, not just matches keywords. For example, if the query is “best ways to improve website speed,” a user likely wants practical tips – so a blog post that gives a step-by-step guide (with context like why each step matters) is ideal. Cover the necessary background or related sub-questions (e.g., explain why image compression helps page speed if you’re recommending that). This intent-focused content is more likely to be selected by AI because it’s genuinely helpful and on-topic.
Distribute Content Across Relevant Platforms: Generative models learn from many sources on the web – not just your site. In fact, large language models are often trained on content from forums, Q&A sites, social media, and more. So, a best practice is to share and repurpose your content on other platforms to increase its footprint. For instance, if you have a great explainer article on your site, consider posting a summary or answering a question on Reddit or Stack Exchange that links back to it. Engage in discussions on industry forums or Quora, providing insights from your content. These activities not only expand your reach to human audiences, but also seed the information in places AIs are crawling. The more an AI sees your authoritative answers on a topic across the web, the more likely it is to include your perspective in its synthesized answers.
Embrace Multimedia and Diverse Formats: Don’t limit GEO efforts to text. AI systems can handle multiple content types (some are multi-modal, and text-based AIs may reference described visuals). Including relevant images, infographics, or even short video transcripts on your pages can enrich the content for AIs and users alike. For example, an AI might mention data from an infographic on your site (“according to an infographic by Company X, 60% of users…”) if it finds it relevant. Visual elements with proper alt text and captions can be parsed by AI, potentially providing bite-sized facts or examples for answers. Plus, multimedia keeps human readers engaged, which indirectly signals to search engines and AIs that your content is valuable.
Leverage Social Media and External Signals: Promote your content on social media and encourage sharing. Generative engines are rumored to take cues from social signals – content that gets widely shared or discussed could be interpreted as more authoritative or relevant. A robust presence on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, or industry-specific networks can amplify your content’s reach. Also, manage your online reputation on review sites or community sites; positive mentions of your brand or content across the web can enhance how AI perceives your authority. In short, a holistic digital presence reinforces to AI models that your content is trusted and worth including.
Maintain Technical SEO Hygiene: Many technical best practices from SEO carry over to GEO. Ensure your site is crawlable and fast. Fix broken links and ensure important content isn’t buried behind navigation that bots (or AI) can’t easily access. Fast page speed and a mobile-friendly design improve user experience and also help AIs retrieve your content efficiently. Use proper meta tags and structured data so that both traditional search bots and AI algorithms can easily find and identify key information. While an AI might not care about your XML sitemap the way Googlebot does, the content still needs to be accessible and well-organized under the hood. A solid technical foundation “future proofs” your site for both SEO and GEO.
Monitor AI Mentions and Evolve: Implement ways to track your presence in generative AI results. This is a new area, but you can start by manually checking how AI platforms respond to relevant queries. For example, periodically ask ChatGPT or Bing Chat a question you’d hope to be featured in, and see if your brand/content is mentioned. There are also emerging tools and methods: analytics platforms can be configured to track traffic from AI sources (e.g., Bing Chat referrals, SGE clicks), and some SEO tools now show if your site was cited in Google’s AI Overview. By measuring where you stand, you can identify what content is working (getting picked up by AI) and what gaps remain. If certain high-value questions are not yielding your content in AI answers, that’s a cue to create new content or improve existing pages. Treat GEO as an ongoing optimization – much like SEO – where you adjust strategy based on what the data shows about your visibility.
Stay Up-to-Date and Adapt: AI search technology is evolving rapidly. New generative search features or algorithms can emerge with little warning. Make it a habit to stay informed via industry blogs, SEO/GEO case studies, and updates from the major search and AI platforms. For example, if Google’s SGE or another engine reveals new criteria for how it selects sources (such as preferring more recent data), be ready to adjust by updating your content frequently. However, avoid chasing every tiny algorithm change – focus on the consistent principle of providing clear, accurate, and user-focused content. If you build a strong foundation, minor shifts in AI behavior won’t drastically undermine your presence. In summary: be agile and ready to experiment, but remain grounded in the fundamentals of good content that serves user needs.
Impact of GEO on Search Rankings and Visibility
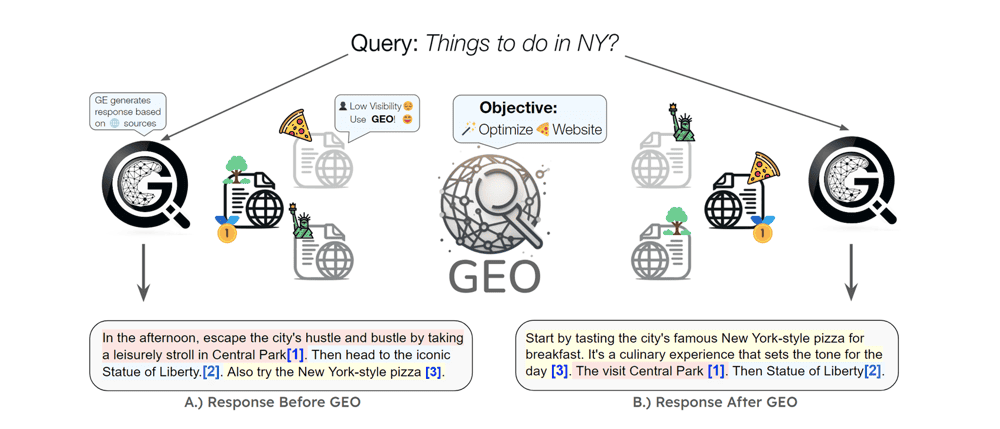
Image: A generative engine’s response to “Things to do in NY?” before and after applying GEO optimizations, as demonstrated by researchers. In the before scenario (A), the AI’s answer only briefly mentioned a New York–style pizza place at the end. After targeted GEO changes to the pizza website, the after scenario (B) shows the AI response now starts by recommending the pizza (with the site cited as a source), highlighting how GEO can boost a brand’s prominence in an AI-generated answer.
The example above illustrates the direct impact GEO can have: by updating and optimizing content, a website significantly increased its visibility in an AI’s answer to a popular query. In that academic case, simply tweaking one site’s content caused an AI to favor that site’s recommendation (the New York-style pizza) much more prominently. This kind of influence is the crux of GEO – it can literally change the narrative that an AI delivers to users.
For website owners and marketers, the rise of generative search means visibility is no longer just about blue links on a SERP, but about being incorporated into answers. When GEO is done well, the payoff is that your brand becomes part of the information an AI provides to users. If an AI assistant or search engine is regularly citing your website as a source of expertise, your brand stays top-of-mind for users in a very competitive digital landscape. Even if the user doesn’t click through immediately, your information has been delivered – which may lead them to seek out your site or product later (or ask the AI follow-up questions involving your brand). In essence, GEO can turn your site into an authority that the AI trusts, thereby recommending you to users on your behalf.
On the flip side, ignoring GEO can have a negative impact on your overall search visibility. If your competitors optimize their content for AI and you don’t, an AI engine might omit your brand from answers altogether. Consider that a user might never see the list of search results where you’re ranking #1 if the AI already gave a full answer. As one expert put it, if your product or content isn’t cited in the AI’s answer, you’re effectively invisible – even if you traditionally rank first on Google. This can be critical for businesses: for instance, a top-ranking blog post that once drove steady traffic could see fewer visitors if users get the answer from an AI without clicking. GEO is about mitigating that risk by keeping your content relevant in an era when answers come directly from AI.
It’s important to note that GEO and SEO are interconnected when it comes to visibility. Often, the content that performs well in traditional search (strong SEO) forms the pool from which generative AI draws information. In fact, Google’s own research indicates a strong correlation between a page’s organic search rank and its likelihood of being included in the AI-powered SGE answer summary. This means good SEO practices (high-quality, authoritative content) enhance GEO, and vice versa. By aligning content with user intent and using GEO techniques, you may also inadvertently improve your regular search rankings, since you’re focusing on clarity and relevance (which search algorithms reward). Thus, implementing GEO tends to have a complementary effect: you maintain or even boost your search engine rankings while also securing presence in AI results.
Finally, GEO’s impact can be measured in terms of brand awareness and credibility. When an AI cites your brand as a source, it’s almost like a third-party endorsement – the AI “chose” your content as helpful. Users hearing your brand in an authoritative answer might trust you more. This kind of visibility is harder to quantify than clicks, but it builds mindshare. Over time, a strong presence in AI-driven answers can drive users to seek out your brand specifically (“I keep hearing about X from ChatGPT’s answers, let me check their site”). In short, GEO helps ensure that the shift to AI search doesn’t leave your site behind – it keeps you visible and relevant as search behavior changes.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in GEO vs. SEO
The roles of AI and machine learning in traditional SEO and in GEO are quite different, reflecting how search itself is evolving:
SEO and Search Engine Algorithms:
In SEO, your primary “audience” (besides human readers) is the search engine’s ranking algorithm. Traditional search engines use algorithms – increasingly augmented by machine learning – to index and rank content. For example, Google uses AI/ML models like RankBrain, BERT, and others to better interpret queries and assess page content for relevance.
However, the end result of those algorithms is still a list of links for the user. In SEO, AI is behind the scenes: it helps the search engine parse language and evaluate pages, but the search results themselves are not AI-generated content, they’re references to content. SEO practitioners historically didn’t need to use AI themselves, aside from understanding that the search engine might value certain signals. That said, AI is now creeping into the SEO toolkit as well – today, many SEOs use AI-powered tools to analyze keywords, suggest content improvements, or even generate first drafts of content.
These tools, like Surfer SEO or Frase, use machine learning to compare your content with top-ranking pages and guide optimizations. So, AI is increasingly a helper in doing SEO, even if it’s not obvious to the end-user.
GEO and AI-Driven Search Engines: In GEO, AI is front-and-center. Generative search engines (like the new Bing Chat or Google’s SGE) use large language models (LLMs) and other AI techniques to actually generate the answer a user sees. They don’t just retrieve and rank links; they compose a response in natural language, often synthesizing information from multiple sources.
This means that when optimizing for these engines, you are effectively trying to make your content amicable to an AI content creator. The AI (powered by ML models) reads and “understands” your text in order to possibly include it in its generated answer. Context and nuance are important – the AI is looking for content that fits the question’s intent and can be woven into a coherent answer. Machine learning models consider not only keyword matching but also semantics, context, and even the tone of content. For example, if the user asks for a comparison, the AI will look for content that has comparative info or pros/cons. If the user asks for a step-by-step solution, the AI will favor content that is structured in steps. GEO thus involves anticipating these needs and formatting your content in ways that align with what the AI model prefers to output. In summary, AI is the new intermediary – you optimize for how the AI sees your site, not just for how a static algorithm scores it.
Direct Use of AI in GEO: There’s also a direct role of AI by the content creators in GEO. Because understanding how AI produces answers is complex, marketers are using AI tools to assist in GEO strategy. Some are using question-answering AI to test their content (“Hey ChatGPT, what would you answer for this query? Did you use my content?”) as a way to audit their visibility. Others leverage AI writing assistants to ensure content is phrased in a conversational, natural way (since that’s how answers are delivered). In advanced cases, companies might even train custom AI models on their own data to see how well their content answers questions, or to provide chatbots that reliably use their verified content. Additionally, generative AI tools can help generate content variations, meta descriptions, or rich snippets that align with likely AI queries.
The key difference is, in GEO the target is an AI – you’re optimizing for an AI’s consumption. That’s fundamentally new. In contrast, traditional SEO never required thinking “How will an AI read this and rephrase it?” but GEO does.
User Experience vs Algorithmic Optimization: In SEO, there has long been a balance between writing for search engines and writing for people. With GEO, writing for the AI and writing for the user start to converge. Why? Because the AI is trying to mimic a helpful human answer. If your content is genuinely helpful to a human, chances are it’s also good for the AI. This is where SEO and GEO align: quality content wins. Google has been pushing this with its AI-infused ranking algorithms (rewarding content that demonstrates expertise, authority, and trust – E-A-T), and now GEO is reinforcing the same idea via AI answers.
Machine learning in generative search is designed to prioritize useful, context-rich content, which means the best GEO strategy is largely to make content deeply useful.
So while the mechanisms differ (SEO’s algorithmic rankings vs. GEO’s AI summarizations), both are increasingly driven by AI/ML considerations – either in how content is ranked or how it is synthesized into answers.
In short, AI and machine learning play a passive role in SEO (as part of search engine algorithms determining rank) but an active role in GEO (the AI is effectively your new content curator and even content consumer). SEO specialists are now also becoming “AI optimizers,” learning how LLMs pick sources. Going forward, expect SEO and GEO to blend as search engines incorporate more AI – optimizing for one will mean optimizing for both.
Potential Benefits and Challenges of Using GEO for Website Optimization
Implementing Generative Engine Optimization can offer many benefits, but it also comes with new challenges. Below we outline the major advantages of GEO, as well as the key obstacles or considerations to keep in mind.
Benefits of GEO
Maintaining Visibility in the AI Era: The primary benefit of GEO is protecting (and extending) your brand’s visibility as user behavior shifts to AI-driven search. Rather than losing traffic because an AI answered a question without showing your link, your content remains visible by being part of that answer. The more your site is sourced in AI responses, the more you stay “top of mind” for customers. In a sense, GEO lets you keep a foothold in an otherwise closed answer box, ensuring you’re not left out of conversations happening on AI platforms.
Improved Trust and Authority Perception: When an AI cites your brand or content as an authoritative source, it’s like a vote of confidence from a very knowledgeable entity. Users tend to trust the answers these AI give, especially if sources are provided. Being one of the cited sources can bolster your brand’s credibility. Companies that anticipate user needs and provide authentic, relevant insights in real-time are rewarded with user trust and loyalty. By optimizing for generative answers, you demonstrate that your content is so good that even the AI relies on it – positioning your brand as a leader or expert on the topic. This can enhance your reputation without a single direct marketing message.
Reaching Users Faster and In Context: GEO can shorten the path between a user’s question and your solution. Instead of hoping a user clicks your link, you reach them within the answer to their query. This can lead to highly qualified traffic – for instance, if an AI mentions your product as “one of the best solutions” for a problem, a user coming to you from that context is already warmed up with a positive impression. Also, AI answers often appear at the very top of search results pages (above all links), so being included there is premium real estate for attention.
Leveling the Playing Field for Smaller Players: Traditional SEO could sometimes be dominated by big companies with massive content budgets and backlink profiles. GEO offers a somewhat more level field. Generative AI doesn’t care how big your brand is; it cares how relevant and helpful your content is. A small business that creates an extremely clear, helpful piece of content can outrank a large competitor within an AI answer if that competitor’s content is fluff or SEO-gamed. In fact, analysts have observed that smaller, niche sites often get cited by AI for very specific queries, because they deliver exactly what the user needs. GEO rewards depth and specificity over breadth. This means up-and-coming brands can gain visibility by being truly useful, even if they can’t beat giants on the Google results page.
(As one author put it, SEO was like a popularity contest, but GEO is like being the helpful expert everyone turns to.)
Enhancing User Experience and Engagement: By focusing on GEO, you inevitably create content that is clearer and more directly useful to users (since that’s what the AI wants too). This has a side benefit: real human visitors who find your content will have a better experience. They’ll get their questions answered without wading through filler. This can lead to higher engagement on your site – users spending more time reading or sharing your content – which further boosts your overall search performance (as engagement can be an SEO signal). Moreover, by providing content in formats that AI can use (like structured FAQs), you’re also making it easier for users to navigate. All of this contributes to a positive feedback loop: great content -> used by AI -> more users trust you -> more traffic and engagement -> improved search performance.
Future-Proofing Your Digital Strategy: Adopting GEO early can put you ahead of competitors in the new search landscape. As generative AI searches become more common, companies who have already tuned their content for AI will reap the benefits while others scramble to catch up. It’s an investment in staying relevant. Industry experts are calling GEO “table stakes” for the near future of marketing – a fundamental component of maintaining visibility in an AI-driven world. Also, GEO work complements your SEO, content marketing, and PR efforts, making all these pieces work together. By integrating GEO, you’re covering all bases: traditional search, AI search, and even voice or chatbot inquiries. This comprehensive approach is vital for success in 2025 and beyond.
Higher Quality Leads and Conversions: When an AI includes your content, it often provides context that pre-qualifies the lead. For example, an AI might answer, “According to YourCompany, which specializes in X, the best practice is to do Y.” A user who clicks through already knows who you are and that you have relevant expertise. By the time they reach your site, they’re more likely to convert (sign up, inquire, purchase) because they’ve essentially been referred by a knowledgeable assistant. In this way, GEO can improve the quality of traffic and leads, not just the quantity.
Challenges of GEO
- Black-Box Nature of Generative AI: One of the biggest challenges is that generative search engines are largely black boxes. Their algorithms for choosing which sources to include (and how) are proprietary and not transparent. With Google SEO, we have years of research and guidelines about how to rank better; with GEO, we’re dealing with new, opaque systems. This means there can be a lot of trial and error. You might optimize content and not see any change in AI citations, without knowing why. The lack of clear “rules” or feedback (AI engines don’t exactly publish GEO guidelines yet) makes it hard to precisely tailor your strategy. Content creators have little control over how their content is ingested and used by AI. We’re essentially optimizing for an audience (the AI) whose preferences we have to infer indirectly.
Potential Loss of Traffic (Zero-Click Results): Generative answers can sometimes lead to zero-click searches, where the user’s query is fully answered on the results page or in the chat interface, and they don’t need to click any website. If an AI gives a comprehensive answer that includes information from your site, the user might feel they got what they needed without visiting you. This is a double-edged sword: your info was used, but you may not get the visit. Website owners reliant on ad impressions or on-site engagement can find this concerning. Indeed, the rise of generative answers has been noted to reduce organic traffic to websites, disrupting the traditional “click for more info” model. GEO tries to mitigate this by at least ensuring your brand is mentioned (so the user knows the source and could follow up), but it doesn’t guarantee a click-through. Businesses have to adjust their KPIs – success might be measured in brand visibility and referral mentions, not just raw traffic.
Accuracy and Control Issues: When an AI is summarizing various sources, there’s a risk it could misrepresent or slightly alter the meaning of your content. It might even pull an outdated snippet. This poses a challenge: your brand could be part of an answer that isn’t entirely correct. For instance, there have been cases where AI tools cited a business but stated an old price, or mixed up facts like business hours. Because you’re not in direct control of the final output, there’s a possibility of misinformation. To combat this, you need to frequently monitor how AI platforms describe your business or cite your content. If you find errors (e.g., the AI says your product has a feature it doesn’t), you may need to correct that info on your site or publicly so that future AI crawls get the right data. This is an ongoing effort and a new kind of reputation management.
Resource and Knowledge Demands: GEO is a new discipline to learn, on top of existing SEO efforts. For businesses with small marketing teams, it can feel overwhelming to add yet another optimization process. There’s time needed to research AI behavior, update content, and possibly create new types of content. The challenge is finding the time and resources for GEO when you’re already busy maintaining SEO, social media, content creation, etc. The key is often to integrate GEO into existing workflows (for example, when you update a blog post for SEO, also tweak it for GEO by adding a summary or Q&A section). Still, the learning curve is real – not everyone is familiar with how language models work. It may require training or consulting with experts to get it right, which is a commitment not every business can easily afford.
Balancing AI Optimization with Human Appeal: There’s a temptation to over-optimize for the AI – like structuring every sentence to please an algorithm – which could make the content less engaging for real readers. Some businesses might go too far and produce content that sounds robotic or is stuffed with facts but has no soul. If human users don’t find your content appealing, it could hurt your brand and even your SEO (since user engagement might drop). Google and other engines also penalize content that is made just for algorithms. The challenge is hitting that sweet spot where content is both AI-friendly and genuinely valuable to a human reader. A good rule is to write for humans first, then fine-tune for AI – ensure the content is readable and helpful, then format or add metadata for the AI. Finding this balance may take some iteration.
Privacy and Strategic Information: GEO sometimes encourages transparency – e.g., sharing detailed answers, case studies, even internal data, because that makes content richer for AI. But businesses must be cautious about what they share publicly. You wouldn’t want to publish sensitive competitive info just to get an edge in AI answers. There is a challenge in deciding how much of your knowledge base to open up. For example, a company might have proprietary research that could bolster its authority if published, but doing so might give competitors an advantage. Each business has to gauge the trade-off between being thorough (for GEO benefit) and keeping certain information private. Using common sense here is key – if you wouldn’t normally put it on your website for humans, be careful about doing it solely to feed the AI.
Measurement and ROI Uncertainty:
Because GEO is new, the analytics around it are underdeveloped.
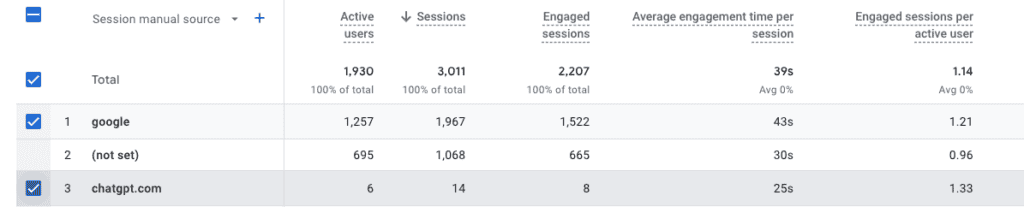
How do you concretely measure success? If an AI mentions you but the user doesn’t click, that might not show up in your web analytics at all. You could be influencing many customers in AI chats and never know it. This makes it hard to attribute conversions or ROI to GEO efforts. While tools are emerging (for example, some analytics can track chat traffic, and SEO platforms are starting to log when a URL is featured in an AI answer), the data is not as rich as what we have for traditional SEO. It may be a while before we have “AI impression” metrics as solid as we have Google Search Console data for SEO.
This challenge means you might need to rely on indirect metrics: overall brand search volume (are more people searching your brand after AI adoption?), referral traffic from AI (if trackable), and anecdotal feedback (customers saying “I found you via ChatGPT”). Justifying GEO effort to stakeholders might be difficult early on due to this fuzzy measurement. Patience is required until reporting catches up with reality.
Despite these challenges, many businesses see GEO as a necessary evolution rather than an optional experiment. The key is to start small, iterate, and learn. Over time, best practices will become clearer, tools will improve, and the balance between SEO and GEO will be more natural. Those who navigate the challenges early will be in a stronger position as AI-driven search becomes the norm.
Future Trends and Predictions for GEO in Web Search and Digital Marketing
The landscape of search is changing rapidly with the infusion of AI, and GEO is at the heart of this transformation. Here are some future trends and predictions for Generative Engine Optimization and how it will shape digital marketing in the coming years:
- Widespread Adoption of AI-Integrated Search: Generative AI in search is not a passing fad – it’s scaling up fast. Major search engines are investing heavily in AI features (for example, Google’s SGE is expanding to more users and queries). Google even expects its AI Overview feature to reach 1 billion users in the near term. Likewise, standalone AI platforms are booming – by 2024, OpenAI’s ChatGPT was receiving over 10 million queries a day, surpassing the query volume of established search engines like Bing. This indicates that huge audiences will be getting information from AI-driven interfaces. For marketers, this means GEO will move from experimental to essential. Optimizing for generative search will become as routine as traditional SEO, simply because that’s where the eyeballs (and questions) are going.
- Conversational and Multimodal Search Experiences: The future of search is looking more like a conversation and less like typing keywords into a box. We’re already seeing users interact with voice assistants and AI chats by asking follow-up questions in natural language. This “conversational commerce” trend means users might carry on a back-and-forth dialogue with an AI when making buying decisions. Additionally, search is becoming multimodal – people can search by image or voice and get AI to interpret it. For example, a user might take a photo of an item and ask an AI to find something similar locally, or show a picture of their room and ask for decoration advice. For GEO, this suggests content
Sources:
Search Engine Journal: Explores how Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) is revolutionizing online search and its implications for SEO professionals. searchenginejournal.com
Google Developer Blog: Provides guidance on how AI-generated content aligns with Google’s approach to delivering helpful search results. developers.google.com
OpenAI Documentation: Offers insights into how language models generate responses, aiding in understanding AI citation and information retrieval processes. platform.openai.com
Bing Blogs: Discusses Bing’s integration of large language models in search and the impact on website traffic and the web ecosystem. blogs.bing.com
Ahrefs SEO Blog: Provides advanced SEO tactics and insights into how backlinks, authority, and contextual relevance influence AI-generated responses. ahrefs.com
Neil Patel’s Digital Marketing Blog: Analyzes the evolving nature of SEO in the context of AI advancements and offers strategies for integrating GEO into existing SEO frameworks.
Reddit SEO Discussions: Features community insights on the effectiveness of optimizing for AI search results and the emerging practice of Generative Engine Optimization. reddit.com
Google Search Console Updates: Introduces tools like Search Console Insights to help content creators understand how audiences discover their site’s content. searchenginejournal.com+3search.google.com+3neilpatel.com+3